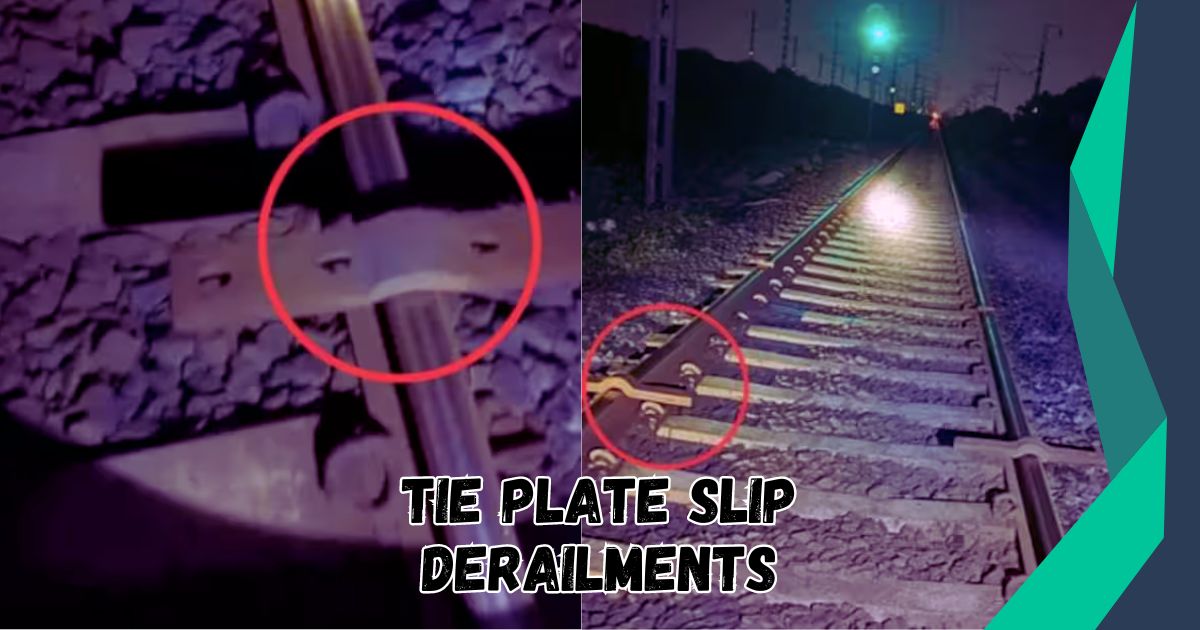
Railroads play a critical role in transporting goods and passengers across vast distances, making track stability a top priority for maintaining operational safety. One key component that helps keep the rails secure is the tie plate, a metal base that sits between the rail and the wooden or concrete railroad ties. However, tie plates can sometimes slip, leading to rail track instability and, in severe cases, derailments.
In this post, we’ll explore the concept of tie plate slip derailment, its causes, consequences, and, most importantly, the best ways to prevent tie plate failures to ensure safer railroad operations.
1. What is Tie Plate Slip Derailment? An Overview of Railroad Safety
A tie plate slip derailment occurs when the tie plates, which are responsible for holding the rails in place on top of the railroad ties, shift out of position. This slippage causes the rails to become misaligned, leading to instability and, potentially, a train derailment. The tie plate ensures that the weight of the train is evenly distributed across the track, and if it slips, the track can no longer effectively support the load of a moving train.
While tie plate slip derailments are not as common as other forms of rail accidents, they can have devastating consequences, especially if they occur at high speeds or in busy rail corridors. Understanding how tie plates work and why they sometimes fail is the first step toward preventing these accidents.
2. How Do Tie Plates Work? The Function of This Critical Rail Component
Tie plates are metal components that sit between the steel rails and the wooden or concrete railroad ties. They are designed to anchor the rails in place, distributing the heavy loads from passing trains across the railroad ties. Tie plates are critical for maintaining the proper gauge (the distance between rails) and preventing the lateral movement of the rails, which can lead to derailment.
Primary Functions of Tie Plates:
- Distribute Load: They help spread the weight of the train across the track structure, ensuring that the pressure is not concentrated in one area.
- Stabilize the Rails: Tie plates secure the rails to the ties, preventing shifting and maintaining the track’s alignment.
- Reduce Wear: By absorbing some of the shock and vibrations caused by train movement, tie plates help prevent excessive wear on the railroad ties.
When tie plates fail or slip, the consequences can be significant, as the track alignment is compromised, leading to potential derailments.
3. Top 5 Causes of Tie Plate Slip Derailments You Need to Know
While tie plates are designed to endure the heavy forces exerted by passing trains, several factors can lead to their slippage or failure. Here are the top five causes of tie plate slip derailments:
1. Poor Maintenance
Regular inspections and maintenance are crucial for keeping railroad infrastructure in top condition. Neglecting to inspect and repair worn-out or loose tie plates can lead to slippage, which may cause derailments.
2. Excessive Train Loads
Tie plates are designed to support a certain weight. When trains exceed the recommended load capacity, the added pressure can cause the tie plates to shift or crack, leading to track instability.
3. Track Vibration and Wear
Over time, the constant movement of trains causes the track structure to vibrate and wear down. This can lead to loose spikes or fasteners, which may allow tie plates to move out of position, particularly if they aren’t properly anchored.
4. Environmental Factors
Weather conditions, such as extreme heat or frost, can cause the rails to expand or contract. These changes put stress on the tie plates, increasing the risk of slippage, especially in regions with fluctuating temperatures.
5. Improper Installation
If tie plates are not properly installed, they are more likely to slip or shift when under pressure. Ensuring that tie plates are securely fastened to both the rails and the ties is critical to preventing derailments.
4. The Consequences of Tie Plate Slip: From Minor Incidents to Major Accidents
While minor tie plate slippage may not result in immediate derailment, even small shifts in the track structure can lead to significant problems if left unaddressed. The consequences of tie plate slip range from minor incidents, such as track buckling, to major accidents, such as train derailments.
Minor Incidents
- Misalignment of the Track: When tie plates slip, the rails can become misaligned, making the track uneven. This can lead to discomfort for passengers and increased wear on the train and track.
- Track Buckling: Excessive heat combined with tie plate slippage can cause the track to buckle, creating dangerous conditions for trains, especially at high speeds.
Major Accidents
- Derailment: In severe cases, a slipped tie plate can cause the rails to move far enough apart that the wheels of the train no longer align with the track, leading to derailment.
- Loss of Cargo: If a freight train derails due to tie plate slippage, it can result in significant financial losses and environmental damage, particularly if the train is carrying hazardous materials.
5. Prevention Measures: How to Minimize the Risk of Tie Plate Slip Derailment
Preventing tie plate slip derailment requires a combination of proactive maintenance, proper installation, and regular inspections. Here are some key prevention strategies:
1. Regular Track Inspections
Routine inspections are essential to identifying early signs of tie plate wear or misalignment. Rail companies should conduct inspections frequently, especially in areas prone to heavy use or extreme weather conditions.
2. Proper Installation and Fastening
Ensuring that tie plates are properly installed and securely fastened can significantly reduce the likelihood of slippage. This includes making sure that rail spikes or clips are tightly secured.
3. Load Management
Monitoring the weight capacity of trains is vital for reducing stress on the track. Overloaded trains put excessive pressure on the tie plates, increasing the chances of failure.
4. Seasonal Maintenance
Seasonal changes, particularly during summer and winter, can affect track stability. Rail operators should adjust their maintenance schedules to account for temperature fluctuations that can lead to rail expansion and contraction, placing additional stress on tie plates.
5. Advanced Monitoring Systems
Technology plays a growing role in preventing rail accidents. Track monitoring systems that useLet me continue from where I left off regarding the prevention of tie plate slip derailment.
5. Advanced Monitoring Systems
Technology has become an essential tool in preventing railway accidents, including those caused by tie plate slips. Track monitoring systems that use sensors and AI-powered analytics can detect early signs of track instability. These systems monitor vibrations, temperature fluctuations, and stress points on the track, alerting railway operators to potential problems before they escalate. Installing these systems along high-risk routes is crucial for preventing derailments due to tie plate failure.
By integrating technology and emphasizing regular maintenance, rail companies can drastically reduce the likelihood of accidents caused by tie plate slip derailments.
6. Maintaining Rail Track Stability: The Role of Tie Plate Inspections and Upkeep
Ensuring the long-term stability of the railway track involves consistent upkeep of all components, particularly tie plates. Here’s why regular tie plate inspections are key:
1. Early Detection of Wear
Regular inspection of tie plates allows for early detection of cracks, bending, or loosening. This can prevent further degradation and help rail operators replace faulty tie plates before they lead to more significant issues, such as misalignment.
2. Lubrication and Maintenance
Tie plates and other track components should be regularly lubricated to reduce wear and minimize friction between the track and the tie plates. This simple maintenance step can extend the lifespan of the tie plates and the track itself.
3. Scheduled Replacement of Worn-Out Components
Proactive replacement of worn-out tie plates can prevent them from becoming a weak point in the rail infrastructure. Replacement should be based on wear patterns, the age of the components, and data collected from monitoring systems.
For more exciting blogs, visit our homepage Magzineco.
7. Conclusion: Enhancing Rail Safety by Addressing Tie Plate Slip Derailments
Tie plate slip derailments pose a serious risk to railroad safety, but they can be largely prevented through a combination of routine maintenance, proper installation, and the integration of modern monitoring systems. Tie plates play an essential role in maintaining track stability and keeping trains on the rails. As technology advances and railroads continue to improve their maintenance practices, the risks associated with tie plate slips can be significantly reduced.
Incorporating proactive measures, such as advanced track monitoring and seasonal maintenance schedules, is critical to ensuring the long-term safety and stability of rail systems worldwide. By addressing tie plate slip derailments, we can protect both cargo and passenger trains, ensuring smoother and safer journeys.
FAQs About Tie Plate Slip Derailments
- What causes tie plate slip derailments?
- Tie plate slip derailments are often caused by poor maintenance, overloaded trains, track vibrations, environmental factors, or improper installation.
- How does a tie plate work in railroads?
- Tie plates serve to stabilize the rails, evenly distribute the load, and reduce wear on the railroad ties, keeping the track aligned and secure.
- Can tie plate slip derailments be prevented?
- Yes, tie plate slip derailments can be prevented through regular inspections, proper installation, load management, and the use of advanced monitoring systems.
- What are the consequences of tie plate slip?
- Consequences can range from track misalignment and buckling to more severe incidents like train derailments and loss of cargo.
- What is the role of technology in preventing tie plate slip derailments?
- Track monitoring systems using sensors can detect early signs of instability and alert operators to potential risks, enabling timely intervention.